
Does Carbon Steel Rust and Why It Happens
Share
Table Of Content
Table Of Content

Carbon steel rusts because it has a lot of iron. Iron reacts with oxygen and water in the air. This reaction makes iron oxide, which we call rust. Carbon steel does not have metals like chromium or nickel. These metals protect stainless steel from rusting. Without this protection, carbon steel is open to things like humidity and salt. These make rust form faster. So, if you ask, "Does Carbon Steel Rust?" the answer is in its makeup and how it reacts to moisture.
Key Takeaways
- Carbon steel rusts quickly because it has a lot of iron. Iron mixes with air and water, causing rust to form.
- Things like moisture, salt, and pollution make rust happen faster. Keep carbon steel dry and clean to stop rust.
- Add protective layers to keep carbon steel safe from rust. You can use zinc-rich paints or epoxy coatings for strong protection.
- Taking care of carbon steel is very important. Clean it often to get rid of dirt and water that cause rust.
- If you see rust, remove it with tools or chemicals. After cleaning, add a protective coat to stop rust from coming back.
Does Carbon Steel Rust? The Science Behind It
What Is Rust?
Rust is a reddish-brown layer on iron or steel. It forms when metal meets water and air. Rust makes the metal weaker by damaging its surface. Scientists group rust by its color and how it forms. For example:
| Rust Color | How It Forms | What It Means |
|---|---|---|
| Yellow | Happens in very wet places over time | Shows long-term water exposure |
| Brown | Dry and crusty from water and air contact | Points to small, specific damage |
| Black | Forms in low water and air areas | Most stable rust, less harmful |
| Red | Forms in salty air like near oceans | Shows risk of rust in salty places |
Knowing these types helps you see how bad rust is and what caused it.
The Chemical Reaction of Rust Formation
Rust happens because of a reaction called oxidation. Iron in carbon steel reacts with water and air to make rust. This process speeds up if salt or pollution is present.
Scientists studied how rust forms. For example:
| Process Name | What Happens |
|---|---|
| Microcell effect | Rust flakes off, exposing fresh metal to corrode. |
| Rust product changes | Loose rust turns into dense rust, making it stable. |
| Surface roughness | Rough surfaces hold rust better than smooth ones. |
These studies explain why rust spreads fast and sometimes falls off, leaving new metal exposed.
Environmental Factors That Contribute to Rust
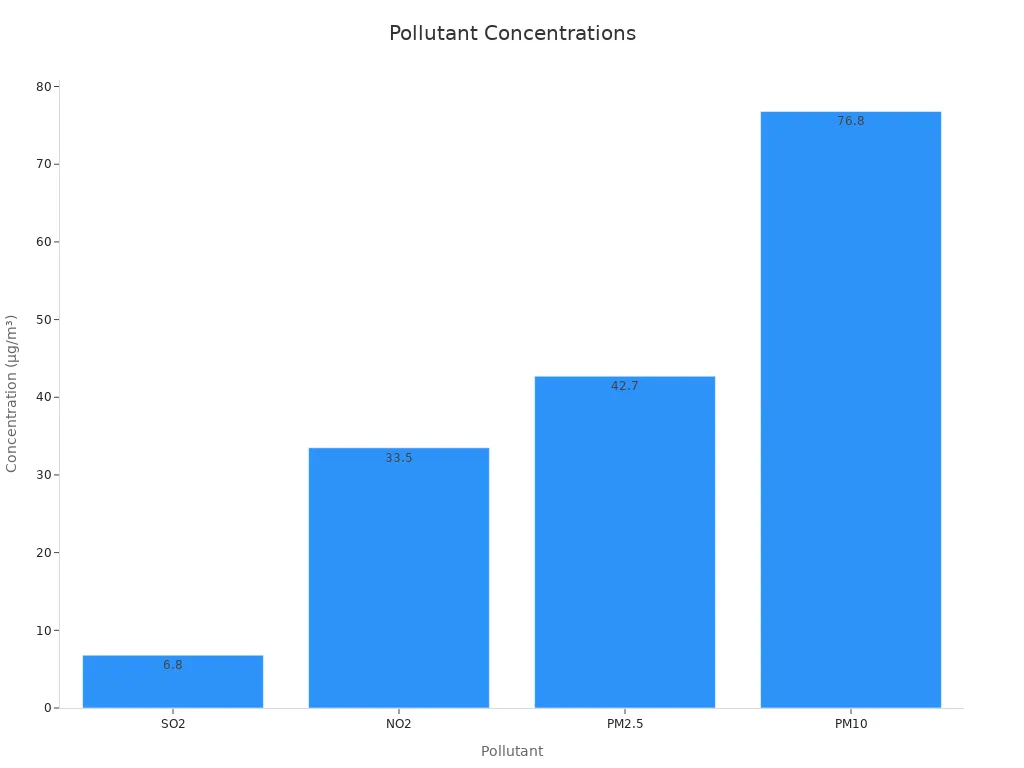
The environment affects how fast rust forms. Wet air, salt, and pollution like sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) make rust worse. A study showed these pollution levels:
| Pollutant | Average Yearly Amount (µg/m³) |
|---|---|
| SO2 | 6.8 |
| NO2 | 33.5 |
| PM2.5 | 42.7 |
| PM10 | 76.8 |
Salt from the ocean is the biggest problem for rust. Wind, rain, and humidity also play a role.
If you live near the sea or factories, your metal items may rust faster. Cleaning and care can help prevent this.
Why Does Carbon Steel Rust Easily?
High Iron Content in Carbon Steel
Carbon steel has a lot of iron, which rusts easily. Iron reacts with air and water, creating rust. This natural process is called oxidation. You cannot stop it, but you can slow it down.
- Carbon steel is mostly made of iron, which rusts quickly.
- It lacks chromium, so it cannot form a protective layer.
- Moist air and salt make carbon steel rust faster.
If you use carbon steel in wet or salty places, rust appears faster. Cleaning and care can help prevent this.
No Protective Chromium Layer
Carbon steel does not have chromium like stainless steel. Chromium helps stop rust by forming a thin shield called chromium oxide. This shield blocks air and water from touching the metal. Without chromium, carbon steel stays open to rust.
Think of chromium as armor for metal. Without it, carbon steel needs extra care. Use coatings or keep it dry to protect it.
Comparing Carbon Steel and Stainless Steel
Carbon steel and stainless steel differ in how they resist rust. Stainless steel has at least 10.5% chromium, which creates a protective layer. Carbon steel has no chromium, so it rusts more easily.
| Steel Type | What It’s Made Of | Rust Resistance |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Mostly iron and carbon | Rusts easily without protection. |
| Stainless Steel | At least 10.5% chromium | Has a protective layer to stop rust. |
Stainless steel needs less care than carbon steel. But with proper care, carbon steel can still work well.
Conditions That Make Rust Form Faster
Moisture and Humidity Exposure
Water and damp air make rust form faster. When carbon steel touches water, even as vapor, it starts to rust. High humidity makes water stick to the steel's surface. This constant dampness helps rust grow quickly. Changes in temperature also add to the problem. For example, warm air cooling down creates water drops on metal. This adds more moisture, speeding up rust. Over time, this cycle worsens rusting, especially in places with bad airflow.
Salt and Pollutants in the Air
Salt and air pollution make rust happen faster. Salt, common near oceans, speeds up rusting by holding water on the steel. This creates a solution that helps rust form. Pollutants like sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) make the air acidic. Acidic air weakens the metal and increases rust. The table below shows how these factors affect rust:
| Environmental Factor | How It Speeds Up Rust |
|---|---|
| Temperature changes | Adds moisture through condensation |
| Salt (near oceans) | Makes rust form much faster |
| High humidity | Speeds up rust growth |
If you live near the sea or factories, your steel items may rust faster. Cleaning and protecting them can help slow this down.
Bad Maintenance Habits
Not taking care of carbon steel makes rust worse. Dirt and grime trap water on the surface, helping rust grow. If you don’t clean or check the steel often, rust can spread without you noticing. Storing steel in wet or stuffy places also adds to the problem. To stop rust, clean the steel, use protective coatings, and store it in a dry spot.
How to Prevent Rust on Carbon Steel
Using Protective Coatings
Protective coatings keep carbon steel safe from rust. They stop water and air from touching the metal. Different coatings work better for different needs.
| Coating Type | Features and Uses | Strength Level |
|---|---|---|
| Zinc-rich primers | Blocks water and air; great for strong protection. | High |
| Epoxy coatings | Sticks well and resists chemicals; good for tough areas. | Very High |
| Acrylic-based paints | Stops rust and looks nice; easy to use. | Moderate |
| Temporary anti-rust | Protects for a short time; simple to apply and remove. | Low |
| Dry coat rust preventatives | Makes a water-repelling layer; gives longer-lasting protection. | Moderate to High |
Pick a coating based on how long you need protection. For lasting safety, use epoxy or zinc-rich primers. For short-term needs, temporary anti-rust coatings are best.
Storing Carbon Steel the Right Way
Good storage stops rust by controlling the environment. Follow these tips to protect your steel:
- Check Often: Look for rust and reapply coatings when needed.
- Keep It Dry: Lower humidity to avoid water on the steel.
- Control Temperature: Keep temperatures steady to stop water drops from forming.
- Choose Safe Spots: Store steel indoors or cover it well if outside.
By keeping the air dry and temperatures steady, you can stop rust. Checking often helps you fix problems early.
Cleaning and Taking Care of Steel
Cleaning removes dirt and water that cause rust. A study on a coastal bridge showed regular care helped it last longer. The bridge faced salty air, but coatings and design changes slowed rust. This shows why cleaning and care are important.
Do the same for your carbon steel. Clean it often to get rid of salt and dirt. Add protective coatings after cleaning to keep rust away. Regular care keeps your steel strong and useful for a long time.
How to Remove Rust from Carbon Steel

Ways to Remove Rust Using Tools
You can remove rust by scraping or grinding it off. This works best for small spots or light rust. Use tools like sandpaper, wire brushes, or power tools to make the job faster.
| Method | What It Does |
|---|---|
| Sandpaper | Scrapes off rust but might leave small scratches. |
| Wire brushes | Removes rust by hand, good for tiny areas. |
| Power tools | Electric grinders or sanders clean bigger areas quickly. |
| Sandblasting | Blasts sand at high speed to clean rust, great for big jobs. |
These methods work well but can harm the steel if overused. Always wear safety gear to protect yourself from flying debris.
Removing Rust with Chemicals
Chemicals can dissolve rust using acids. This is great for heavy rust or large surfaces. You can soak the steel or apply the solution with a cloth. Common chemicals include phosphoric acid and hydrochloric acid.
- Phosphoric acid: Changes rust into a black layer that protects.
- Hydrochloric acid: Quickly removes rust but needs careful handling.
- Electrolytic removal: Uses electricity to clean rust, good for detailed shapes.
- Pickling: Dips steel in a chemical bath to clean rust, used for big systems.
Chemical methods save time but need safety steps. Work in open spaces and wear gloves and goggles.
Stopping Rust After Cleaning
After cleaning rust, protect the steel to stop it from coming back. Here are some tips:
- Add a coating: Use paint, oil, or dry sprays to block water.
- Store in dry places: Keep steel in areas with low moisture.
- Use sacrificial metals: Attach a metal that rusts first to protect the steel.
- Blueing: Treat steel with chemicals to form a protective layer.
- Wrap with VCI materials: Use wraps that release rust-preventing vapors.
Clean and check your steel often to keep it safe. These steps help your carbon steel last longer and stay rust-free.
Carbon steel rusts because it has a lot of iron. Iron reacts with air and water, causing rust to form. It lacks chromium, so it cannot block rust naturally. Wet air, salt, and pollution make rust happen faster. To stop rust, use coatings, store steel in dry places, and clean it often. If rust appears, remove it with tools or chemicals. After cleaning, protect the steel to stop more rust. With good care, carbon steel stays strong and useful for a long time. So, does carbon steel rust? Yes, but care and upkeep make a big difference.
FAQ
Why does carbon steel rust faster than stainless steel?
Carbon steel rusts quickly because it has no chromium. Chromium creates a shield that stops air and water. Without this shield, carbon steel reacts fast with moisture, causing rust.
Can rust on carbon steel be stopped completely?
You cannot fully stop rust, but you can slow it. Apply protective coatings, keep the steel in dry spots, and clean it often. These actions limit contact with water and air, which cause rust.
Is rust harmful to carbon steel?
Rust damages carbon steel by breaking down its surface. Over time, it weakens the metal and makes it less strong. If ignored, rust can lead to serious damage or failure.
How often should carbon steel be cleaned to avoid rust?
Clean carbon steel monthly if it faces moisture or dirt. In salty or damp areas, clean it every week. Regular cleaning removes things that help rust grow.
What is the best way to keep carbon steel safe?
Store carbon steel in a dry place with good airflow. Avoid areas with high humidity or temperature shifts. Use covers or coatings to protect it from air and water.
Tip: Check stored steel often for rust. Finding rust early makes it easier to fix.

1 comment
монстр трак