
What is SUS304 Stainless Steel
Share
Table Of Content
Table Of Content

SUS 304 stainless steel is one of the most popular austenitic stainless steels you’ll encounter. Its composition includes 18% chromium and 8% nickel, which give it excellent corrosion resistance and make it highly versatile. This material is classified under the Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS), ensuring its quality and consistency. You’ll find SUS 304 stainless steel widely used in industries due to its strength and adaptability.
Key Takeaways
-
SUS304 stainless steel has 18% chromium and 8% nickel. This makes it resist rust and useful for many purposes.
-
It is very strong, with strength between 515 and 625 MPa. This makes it good for tough jobs and harsh places.
-
SUS304 is simple to weld and shape into designs. It is used in building, food factories, and car-making.
-
SUS304 works well in most places but not in strong acids or salty areas. In such cases, SUS316 is a better choice.
-
Cleaning and care can make SUS304 last longer. This keeps it shiny and free from rust.
Chemical Composition of SUS304 Stainless Steel

Key Elements
Chromium and its role in corrosion resistance
Chromium plays a vital role in the corrosion resistance of SUS304 stainless steel. It forms a thin, protective oxide layer on the surface, which prevents rust and degradation. With a chromium content ranging from 18% to 20%, this steel grade offers excellent durability in various environments. This high chromium percentage ensures that the material remains resistant to oxidation, even when exposed to moisture or air.
Nickel and its contribution to strength and ductility
Nickel enhances the strength and ductility of SUS304 stainless steel. It stabilizes the austenitic structure, allowing the material to maintain its toughness even at low temperatures. The nickel content, typically between 8% and 10.5%, also improves the steel's ability to withstand mechanical stress without cracking or breaking. This makes it ideal for applications requiring both flexibility and durability.
Other elements like carbon, manganese, and silicon
In addition to chromium and nickel, SUS304 stainless steel contains small amounts of carbon, manganese, and silicon. Carbon, limited to 0.08%, increases hardness but must remain low to avoid compromising corrosion resistance. Manganese (up to 2%) improves strength and wear resistance, while silicon (up to 1%) enhances oxidation resistance and structural integrity.
Comparison with Other Grades
SUS304 vs SS304 in terms of composition
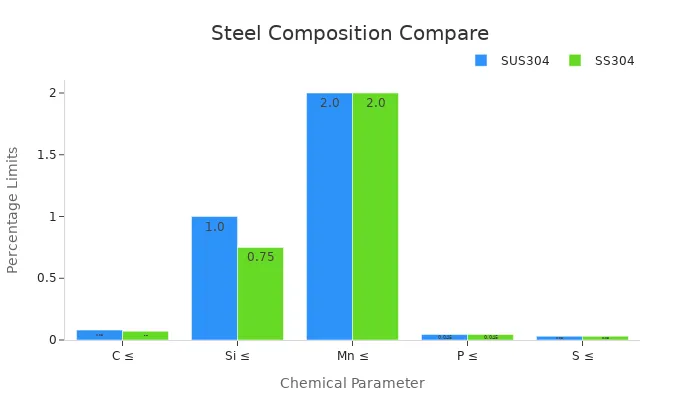
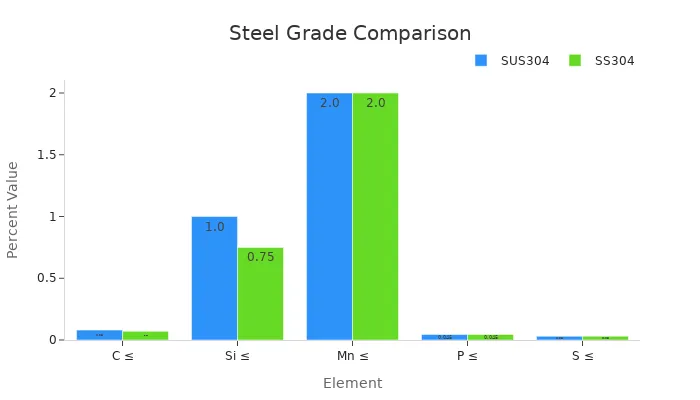
SUS304 and SS304 are nearly identical in composition, but slight differences exist due to regional standards. The table below highlights these variations:
|
Element |
SUS304 |
SS 304 |
|---|---|---|
|
Carbon (C) |
≤ 0.08 |
≤ 0.07 |
|
Silicon (Si) |
≤ 1.00 |
≤ 0.75 |
|
Manganese (Mn) |
≤ 2.00 |
≤ 2.00 |
|
Chromium (Cr) |
18.00-20.00 |
17.5-19.5 |
|
Nickel (Ni) |
8.00-10.50 |
8.0-10.5 |
These differences are minor and do not significantly affect the performance of either grade. However, SUS304 adheres to Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS), while SS304 follows American standards.
SUS304 vs SUS316 and the role of molybdenum
SUS316 contains molybdenum, which provides enhanced corrosion resistance, especially in chloride-rich environments. This makes SUS316 more suitable for marine and chemical applications. However, SUS304 remains more cost-effective and versatile for general use. The chart below illustrates the compositional differences between SUS304 and SS304:
Mechanical Properties of SUS304 Stainless Steel
Strength and Durability
Tensile strength and yield strength
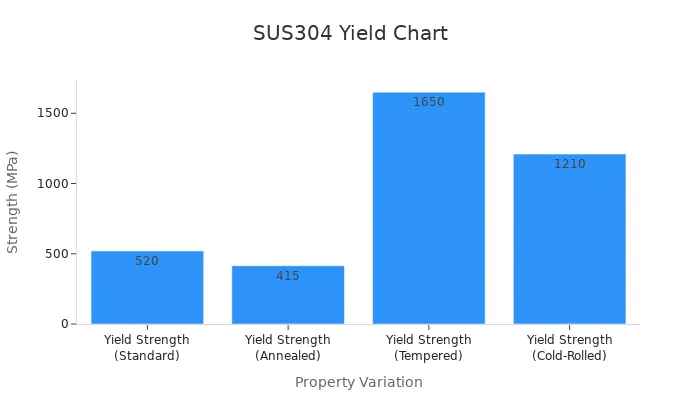
When it comes to strength, SUS304 stainless steel stands out as a reliable material. Its tensile strength ranges from 515 MPa to 625 MPa, making it suitable for applications requiring high durability. The yield strength varies depending on the treatment process, as shown in the table below:
|
Property |
Value (MPa) |
|---|---|
|
Yield Strength (Standard) |
520 |
|
Yield Strength (Annealed) |
415 |
|
Yield Strength (Tempered) |
1650 |
|
Yield Strength (Cold-Rolled) |
1210 |
This versatility allows you to select the appropriate treatment for your specific needs. For example, tempered SUS304 offers exceptional strength for heavy-duty applications, while annealed SUS304 provides a balance of strength and flexibility.
Elongation and ductility
SUS304 stainless steel exhibits excellent elongation properties, which means it can stretch significantly before breaking. This characteristic ensures that the material can withstand mechanical stress without cracking. Its ductility makes it ideal for forming and shaping into complex designs, such as in construction or automotive components.
Hardness and Toughness
Brinell and Rockwell hardness ratings
The hardness of SUS304 stainless steel is measured using Brinell and Rockwell scales. It typically scores between 123 and 201 on the Brinell scale and falls within the HRB 70-90 range on the Rockwell scale. These ratings indicate that the material offers a good balance of hardness and machinability, making it easy to work with while maintaining durability.
Resistance to wear and deformation
SUS304 stainless steel resists wear and deformation effectively, even under heavy loads. Its ability to maintain structural integrity in demanding conditions makes it a preferred choice for industrial and consumer applications. You can rely on this material for long-term performance in environments where mechanical stress and abrasion are common.
Key Characteristics of SUS304 Stainless Steel
Corrosion Resistance
Performance in various environments
SUS304 stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance in clean and moderate conditions. Its chromium-rich composition forms a protective oxide layer, shielding the material from rust and oxidation. This makes it ideal for environments with exposure to moisture, air, or mild chemicals. For example, you can rely on it for kitchenware, food processing equipment, and architectural applications.
|
Characteristic |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Corrosion Resistance |
Excellent in clean and moderate conditions due to a chromium-rich composition. |
|
Susceptibility to Pitting |
Vulnerable in high pollution or acidic environments, especially near coastal regions. |
|
Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC) |
Can occur at temperatures as low as 50°C with chloride exposure, leading to sudden failures. |
|
Crevice Corrosion |
Develops in confined spaces, particularly in marine applications, where chlorides accumulate. |
|
Recommended Alternatives |
For aggressive environments, consider 316 stainless steel or duplex stainless steels. |
|
Maintenance Recommendations |
Regular cleaning and design strategies to minimize crevices can enhance longevity. |
Limitations in highly acidic or chloride-rich conditions
While SUS304 stainless steel performs well in many environments, it has limitations in highly acidic or chloride-rich conditions. Chlorides, such as those found in seawater or de-icing salts, can cause pitting or crevice corrosion. Stress corrosion cracking (SCC) may also occur at elevated temperatures, especially when exposed to chlorides. For these scenarios, you should consider alternatives like SUS316, which contains molybdenum for enhanced resistance.
Weldability and Fabrication
Ease of welding and forming
SUS304 stainless steel is highly weldable and easy to fabricate. You can use all standard fusion welding methods, with or without filler metals. Its excellent machinability allows you to shape it into complex designs, making it suitable for industrial and consumer applications. To improve machinability, keep cutting edges sharp and use appropriate coolants or lubricants during the process.
Common welding techniques
You can weld SUS304 using techniques like TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) and MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding. For heavy welded sections, post-weld annealing may enhance corrosion resistance, though this step is unnecessary for SUS304L. The AS 1554.6 standard pre-qualifies welding of SUS304 with Grade 308 rods or electrodes, ensuring reliable results.
Physical Properties
Thermal conductivity and expansion
SUS304 stainless steel exhibits moderate thermal conductivity and expansion. At room temperature (25°C), its thermal conductivity measures 16 W/m·K. This value decreases to 8 W/m·K at cryogenic temperatures and increases to approximately 11 W/m·K at 300°C. Its thermal expansion rates vary with temperature, as shown below:
|
Thermal Expansion (10-6/K) |
Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) |
|---|---|
|
16.8 (100℃) |
|
|
17.8 (20-300℃) |
|
|
18.4 (20-500℃) |
|
Electrical conductivity and magnetism
SUS304 stainless steel has low electrical conductivity, making it less suitable for electrical applications. It is also non-magnetic in its annealed state, which is beneficial for applications requiring minimal magnetic interference. However, cold working may induce slight magnetism.
Applications of SUS304 Stainless Steel

Industrial Applications
Use in chemical processing and food industries
You’ll find SUS304 stainless steel widely used in chemical processing and food industries due to its exceptional properties. Its corrosion resistance and structural integrity make it ideal for demanding environments. For example:
-
In chemical processing, it’s used in heat exchangers for sulfuric acid manufacturing. This showcases its ability to withstand aggressive conditions without degrading.
-
In the food industry, it plays a critical role in milk pasteurization equipment. Its smooth surface ensures sanitation and precise temperature control. Additionally, it’s a key material in brewing and bottling operations, where maintaining food safety is essential.
These applications highlight how SUS304 stainless steel supports both efficiency and safety in industrial processes.
Applications in construction and architecture
In construction and architecture, SUS304 stainless steel stands out for its durability and aesthetic appeal. You can see it in building facades, railings, and structural components. Its resistance to corrosion ensures long-lasting performance, even in outdoor environments. Architects also favor it for its sleek, modern appearance, which enhances the visual appeal of buildings. Whether it’s a skyscraper or a pedestrian bridge, SUS304 delivers both strength and style.
Consumer Applications
Kitchenware and household appliances
SUS304 stainless steel is a staple in your kitchen. It’s used in cookware, cutlery, and sinks because of its resistance to rust and ease of cleaning. Its non-reactive surface ensures that your food remains safe and untainted. Household appliances like refrigerators and dishwashers also rely on SUS304 for its durability and sleek finish. This makes it a practical and attractive choice for everyday use.
Automotive and transportation uses
In the automotive and transportation sectors, SUS304 stainless steel plays a vital role. You’ll find it in exhaust systems, fuel tanks, and decorative trims. Its ability to withstand high temperatures and resist corrosion ensures reliable performance. Additionally, its lightweight nature contributes to fuel efficiency, making it a preferred material for modern vehicles.
SUS304 Stainless Steel vs Other Grades
SUS304 vs SS304
Differences in standards and naming conventions
You might wonder about the difference between SUS304 and SS304. Both refer to the same material but follow different standards. SUS304 adheres to Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS), while SS304 complies with American standards like ASTM. These naming conventions reflect regional preferences rather than significant differences in the material itself.
The table below highlights how these standards compare:
|
Grade |
UNS No |
Old British |
Euronorm |
Swedish SS |
Japanese JIS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
304 |
S30400 |
304S31 |
58E |
1.4301 |
SUS 304 |
Similarities in properties and applications
Both SUS304 and SS304 share nearly identical properties. They exhibit excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for environments with moisture or mild chemicals. Their mechanical properties, such as tensile strength and yield strength, also align closely. For example:
|
Property |
SUS304 |
SS 304 |
|---|---|---|
|
Density |
7.93 g/cm³ |
7.93 g/cm³ |
|
Melting Point |
1400-1450 °C |
1398-1454 °C |
|
Thermal Conductivity |
460-502 W/m·K |
500 J/(Kg·K) at 0-100°C |
These similarities make both grades interchangeable for most applications, including kitchenware, construction, and automotive components.
SUS304 vs SUS316
Enhanced corrosion resistance of SUS316 due to molybdenum
SUS316 stands out for its superior corrosion resistance, thanks to the addition of molybdenum (2-3%). This element enhances its ability to withstand chloride-rich environments, such as marine or chemical settings. In contrast, SUS304 performs well in general conditions but may struggle in aggressive environments.
|
Property |
SUS304 |
SUS316 |
|---|---|---|
|
Corrosion Resistance |
Moderate |
Superior |
|
Chemical Composition |
16-18% Cr, 8-10.5% Ni |
16-18% Cr, 10-14% Ni, 2-3% Mo |
Cost and application differences
You’ll find SUS316 more expensive than SUS304 due to its enhanced composition. While SUS304 suits general-purpose applications, SUS316 excels in specialized fields like marine engineering, medical devices, and food processing. If cost is a concern, SUS304 remains a versatile and economical choice.
SUS304 vs Other Grades
Comparison with ferritic and martensitic stainless steels
Ferritic and martensitic stainless steels differ significantly from SUS304. Ferritic steels, like grade 430, offer moderate corrosion resistance but lack the ductility of SUS304. Martensitic steels, such as grade 410, provide high strength and hardness but compromise on corrosion resistance.
|
Grade |
Yield Strength 0.2% Proof (MPa) min |
|
|---|---|---|
|
304 |
620 |
289 |
|
304L |
586 |
241 |
Advantages and disadvantages of SUS304 over other grades
SUS304 stainless steel offers a balanced combination of strength, corrosion resistance, and affordability. Unlike ferritic grades, it maintains excellent ductility and weldability. Compared to martensitic steels, it resists rust more effectively. However, it may not match the hardness of martensitic grades or the cost-effectiveness of ferritic options for specific uses.
SUS304 stainless steel stands out for its exceptional corrosion resistance, strength, and durability. Its high chromium content forms a protective layer, ensuring long-lasting performance in diverse environments. You’ll find it used in industries like food processing, healthcare, and construction due to its reliability and ease of fabrication. With tensile strength ranging from 515 to 625 MPa, it balances affordability with performance. Whether in industrial piping or household appliances, its versatility makes it an indispensable material for countless applications.
FAQ
What makes SUS304 stainless steel different from regular steel?
SUS304 stainless steel contains chromium and nickel, which give it corrosion resistance and durability. Regular steel lacks these elements, making it prone to rust and wear. You’ll find SUS304 ideal for environments where moisture or chemicals are present.
Can SUS304 stainless steel rust?
SUS304 resists rust due to its chromium content. However, in chloride-rich or highly acidic environments, it may develop pitting or crevice corrosion. Regular cleaning and maintenance can help you prevent this.
Is SUS304 stainless steel magnetic?
In its annealed state, SUS304 is non-magnetic. Cold working, such as bending or rolling, may induce slight magnetism. If you need non-magnetic properties, you should avoid cold working the material.
How do you clean SUS304 stainless steel?
Use warm water, mild soap, and a soft cloth to clean SUS304. Avoid abrasive cleaners or steel wool, as they can scratch the surface. Regular cleaning helps maintain its shine and prevents corrosion.
What are the limitations of SUS304 stainless steel?
SUS304 performs well in most conditions but struggles in chloride-rich or highly acidic environments. For marine or chemical applications, you should consider alternatives like SUS316, which offers better corrosion resistance.
